如果你有一个程序,需要在后台不断的运行,那一个托管工具,肯定必不可少。今天跟大家介绍的是supervisor,也许你会说现在不是systemd的天下啦。没错的,它更为强大,而且ubantu已经自带了它。但是supervisor还是有其存在的意义,我们今天就主要来介绍下它。
由于它是用python写的,所以有两种安装方式。
apt-get install supervisor
pip install supervisor
我选择的是pip安装方式。
这样子就算是安装成功了。然后我们来看下它的默认配置。
echo_supervisord_conf
图1
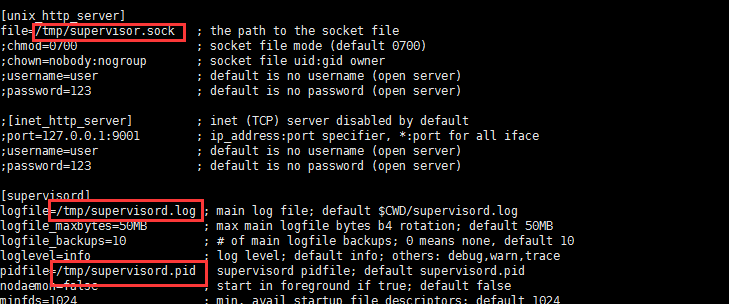
图2
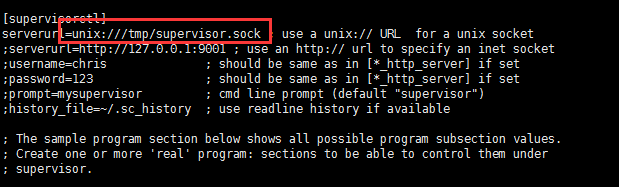
图3
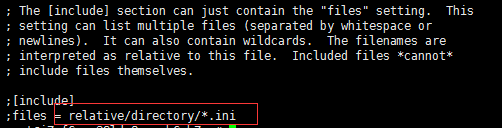
其实我们不需要配置这么多东西,修改图片截图的部分,再保留一些有用的即可。为什么要修改图中的部分,因为tmp是一个临时文件,不懂什么时候会被删除,一旦被删除,就会出现错误,所以我们把它的位置修改了以及修改了配置文件的路径,便于统一管理。
mkdir /etc/supervisor
vi /etc/supervisor/supervisord.conf
首先创建supervisor文件夹,并且在其中创建配置文件supervisord.conf,写入以下配置。
[unix_http_server]
file=/var/run/supervisor.sock ; UNIX socket 文件,supervisorctl 会使用
;chmod=0700 ; socket 文件的 mode,默认是 0700
;chown=nobody:nogroup ; socket 文件的 owner,格式: uid:gid
;[inet_http_server] ; HTTP 服务器,提供 web 管理界面
;port=127.0.0.1:9001 ; Web 管理后台运行的 IP 和端口,如果开放到公网,需要注意安全性
;username=user ; 登录管理后台的用户名
;password=123 ; 登录管理后台的密码
[supervisord]
logfile=/var/run/supervisord.log ; 日志文件,默认是 $CWD/supervisord.log
logfile_maxbytes=50MB ; 日志文件大小,超出会 rotate,默认 50MB
logfile_backups=10 ; 日志文件保留备份数量默认 10
loglevel=info ; 日志级别,默认 info,其它: debug,warn,trace
pidfile=/var/run/supervisord.pid ; pid 文件
nodaemon=false ; 是否在前台启动,默认是 false,即以 daemon 的方式启动
minfds=1024 ; 可以打开的文件描述符的最小值,默认 1024
minprocs=200 ; 可以打开的进程数的最小值,默认 200
; the below section must remain in the config file for RPC
; (supervisorctl/web interface) to work, additional interfaces may be
; added by defining them in separate rpcinterface: sections
[rpcinterface:supervisor]
supervisor.rpcinterface_factory = supervisor.rpcinterface:make_main_rpcinterface
[supervisorctl]
serverurl=unix:///var/run/supervisor.sock ; 通过 UNIX socket 连接 supervisord,路径与 unix_http_server 部分的 file 一致
;serverurl=http://127.0.0.1:9001 ; 通过 HTTP 的方式连接 supervisord
; 包含其他的配置文件
[include]
files = /etc/supervisor/conf.d/*.conf ; 可以是 *.conf 或 *.ini
接着保存,然后创建我们的配置文件目录,并且启动配置文件。
mkdir /etc/supervisor/conf.d
supervisord -c /etc/supervisor/supervisord.conf
添加一个我们测试的配置文件,然后填入我们的内容。
vi /etc/supervisor/conf.d/test.conf
[program:test]
directory = /root ; 运行的目录
command=python test.py ;需要执行的命令
user=root ; 用哪个用户启动
autostart = true ; 在 supervisord 启动的时候也自动启动
startsecs = 5 ; 启动 5 秒后没有异常退出,就当作已经正常启动了
autorestart = true ; 程序异常退出后自动重启
startretries = 3 ; 启动失败自动重试次数,默认是 3
redirect_stderr = true ; 把 stderr 重定向到 stdout,默认 false
最后启动我们刚刚添加那个配置
supervisorctl start test
 到了这里,我们就简单的配置完一个程序的托管了。紧接着我们来测试下是否有效。
到了这里,我们就简单的配置完一个程序的托管了。紧接着我们来测试下是否有效。
ps -ef|grep test
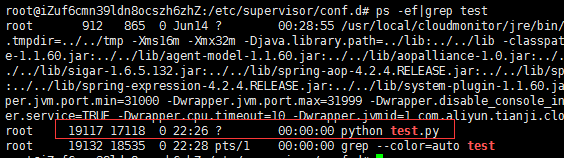 我们把它的进程杀掉,看下还会不会存在。
我们把它的进程杀掉,看下还会不会存在。
kill -s 9 19117
ps -ef|grep test
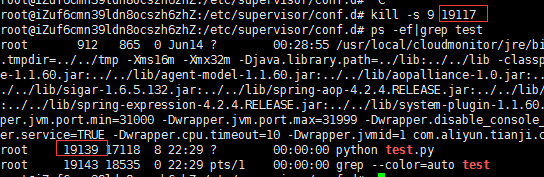 发现我们把之前的进程杀掉后,又起来了一个新的,证明supervisor正在保证我们的程序不会停掉,到此大工告成。
发现我们把之前的进程杀掉后,又起来了一个新的,证明supervisor正在保证我们的程序不会停掉,到此大工告成。
为什么我最近会学习这个,因为打算用nginx加supervisor加flask搭建一个站点。所以下次我会分享nginx的配置,主要是反向代理。
在这边说明下supervisor分为两个部分:supervisord 服务端 即主进程 和supervisorctl 客户端 即启动supervisor的命令行窗口。
supervisord命令:
service supervisord start
service supervisord restart
service supervisord stop
supervisorctl命令:
supervisorctl status
查看当前所有程序的运行状态。status后面可以加上具体某个程序的名字来看其状态。
supervisorctl start xxx
启动xxx程序。如果xxx是all的话,表明启动所有程序。
supervisorctl restart xxx
以上同理
supervisorctl stop xxx
以上同理
supervisorctl reload
重新加载配置。原来正在运行的程序会全部重启。
supervisorctl update
加载新的配置,原来正在运行的程序不会重启。
supervisorctl tail -f shadowsocks stderr
查看标准错误输出。
supervisorctl fg xxx
把某个进程在前台显示,经常可以看一些程序的输出,特别好用。
supervisorctl help
查看帮助